There are many ways to determine how well a computer can perform 3D rendering and Corona Benchmark is one of them. This test is offered by Chaos Corona developers (previously, Corona Renderer) and is based on the 1.3 version of their rendering engine. To start the Corona benchmark test, download it from the official website, unpack the archive, and run the executable file. A Chaos Corona window will open and rendering of a standard scene will start. Once complete, you will see the results and will be able to save or share them online.
You can download Corona 1.3 Benchmark for Windows
here. You can see the results of other users
here.
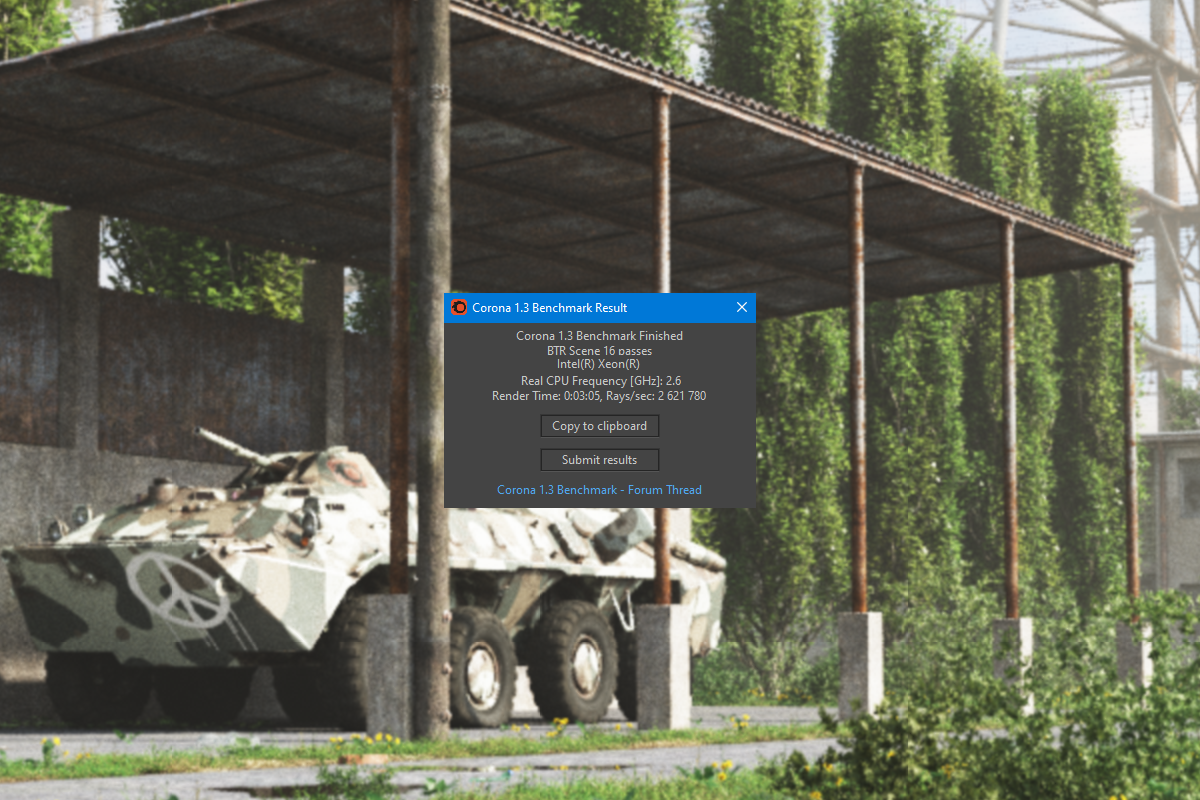
What does this result mean? The less it took to render the test scene, the better. Corona is a CPU-based rendering engine which utilizes a processor instead of a graphics card in its calculations. The power of each processor’s core plays a big role, though the amount of cores is just as crucial; often, many small cores show better results than a handful of powerful ones. If you look at the user score table, you’ll see that the top results are achieved with arrays of server CPUs working as one.
Is it accurate?
The simple answer is: it’s complicated. The Corona Benchmark test is a good way to compare different processors. However, if you open the results for any specific CPU model, you will see widely different results with completion time varying by dozens of seconds or even minutes. This happens because different hardware setups can make rendering faster or slower. RAM volume is one of such critical elements; when Corona runs out of usable RAM, it starts using hard drive space, which is much slower. The frequency RAM runs on can also affect the results. Overclocking increases the power of each CPU core and can raise the scores by 10-30%. Most of the score submitters are overclockers, for whom having a high score is the main point of running the test; they don’t necessarily care about how well the actual rendering goes. Others are render farm owners, who can assemble systems most suitable for rendering but not much else.
Another thing to note, the benchmark is based on a very old version of the Corona rendering engine and is no longer representative of how the process works. Having a lower Corona benchmark score doesn’t always mean your renders in Corona 8 will be slow. The engine underwent years of upgrades and overhauls, adding new features and improving the algorithms. There are ways to make rendering faster by optimizing the projects and tinkering with settings. This means even a less powerful computer can provide impressive results.
What else to look at?
When choosing a new computer or determining how suitable your workstation is for rendering in Corona, it is advisable to look up more than one benchmark. V-Ray, Corona’s main competitor, offers its own benchmark that updates with every new release. V-Ray 5 Benchmark is available from the Chaos Group website and lets you test CPUs and GPUs. Make sure to compare results only of the same version of the benchmark; they are more representative of how well your new computer will do in V-Ray rendering compared to the old one. Blender Benchmark also offers both CPU and GPU testing.
The most popular tool to determine CPU power, however, is Cinebench. This benchmark was developed by MAXON, the company behind Cinema 4D and Redshift. CPU developers chase high Cinebench scores when engineering new models of their flagman processors. The benchmark gets updated every few years to keep up with the advancements in hardware development. At the time of writing this article, the latest version is Cinebench R23; for older CPU models, Cinebench R20 and R15 scores can still be easily found.
Combining these benchmarks with Corona Benchmark test scores will give you a better understanding of how suitable your computer is for 3D rendering. If upgrading your hardware feels like an unaffordable investment, consider using a render farm instead. You can test Megarender cloud render farm for free by creating an account and packaging your project with a special plugin. For further guidelines, refer to our Quick start database or ask in chat.